Knowing the types of cinematographic shots is essential to learn to tell stories. Each type of shot transmits a different sensation and message, helps us in our narrative and manages to impact the viewer in a different way.
If you want to know in depth the types of shots that are used in the cinema, what you can transmit with each one and learn to master this fascinating language, continue with me because we are going to see them one by one with examples included.
WHAT TYPES OF FILM SHOTS ARE THERE?
The types of planes that are used in the cinema are divided, mainly, according to the portion of the scene that we include in the frame, the angle from which the image is recorded and the point of view.
Although we are going to see them one by one, here is a summary of all the plans according to their classification:
- Types of planes according to the frame
- big general shot
- General plane
- Flat figure or whole
- American flat or 3/4 flat
- mid shot
- short medium shot
- Foreground
- extreme close up
- Detail plan
- flat set
- Types of planes according to the angle (or angulation)
- Cenital plane
- Chopped flat
- Frontal or normal plane
- low angle shot
- nadir plane
- foreshortening plane
- dorsal plane
- profile plane
- dutch plane
- Types of planes according to the point of view
- target plane
- subjective shot
- indirect plane
In the following sections we will see them in detail and with examples so that you can learn to compose a scene.
TYPES OF CINEMATOGRAPHIC SHOTS ACCORDING TO THE FRAME
When we talk about types of shots according to the frame, we are talking about the portion that the scene occupies within the frame. Depending on the amount of scene that occupies, we will transmit some sensations or others.
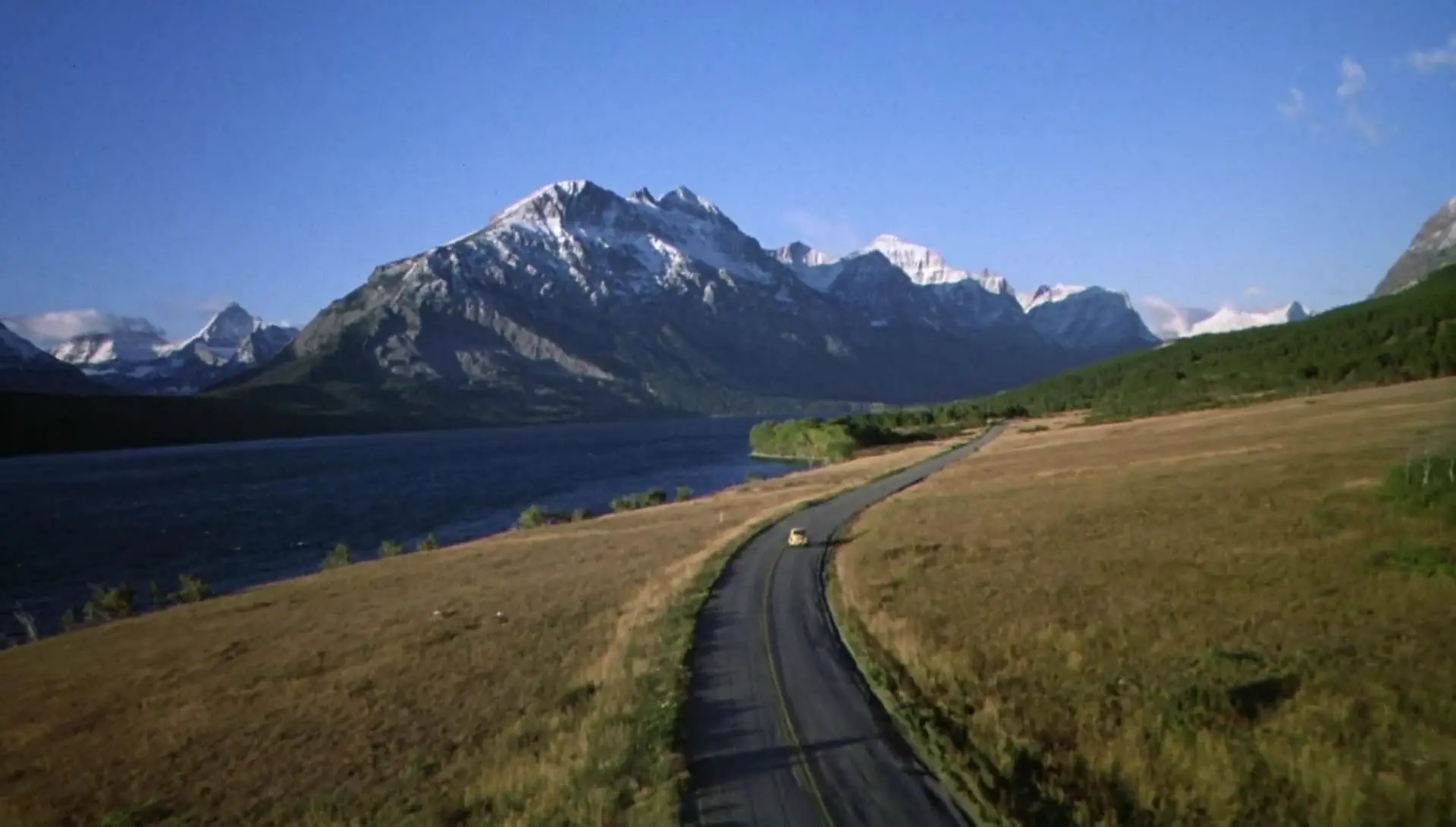
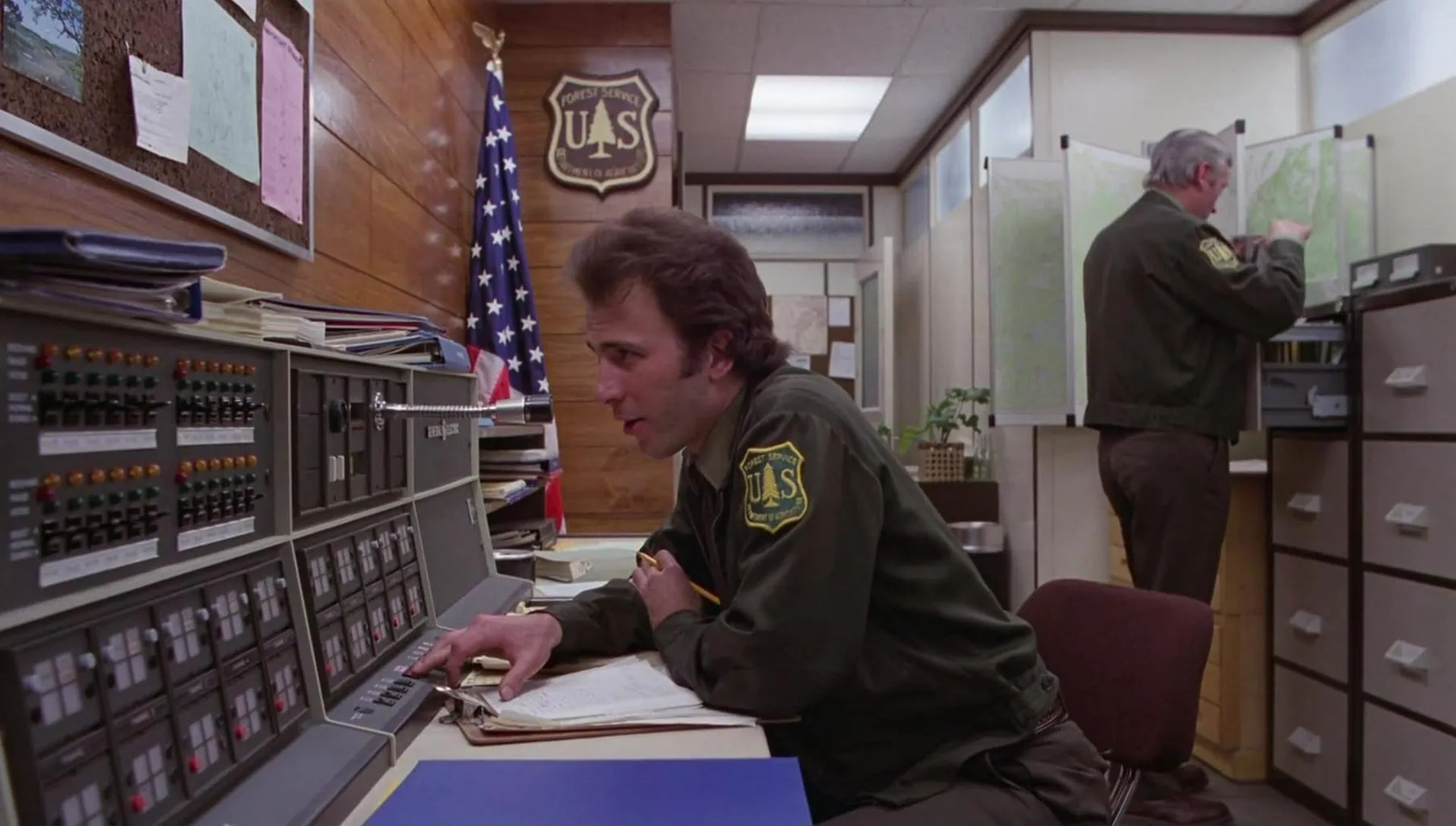
BIG GENERAL SHOT
It is a very open plane that is used mainly to give the viewer a context of place. It is often used to present and describe a place. In it the landscape or the environment is the protagonist and the subjects do not appear or are not distinguished.
The large general shot is used a lot at the beginning of movies or series to give us context with ultra-wide-angle lenses, drone-type aerial views , etc.
Here you can see an example of a great wide shot used in the first frames of the movie "The Shining" ? . Throughout this article I will give you more examples of this film, so if you see it again, you will have to do the exercise of identifying the shots while you watch it.
That is if you manage to see it in its entirety without covering your eyes hehehe…

GENERAL PLANE
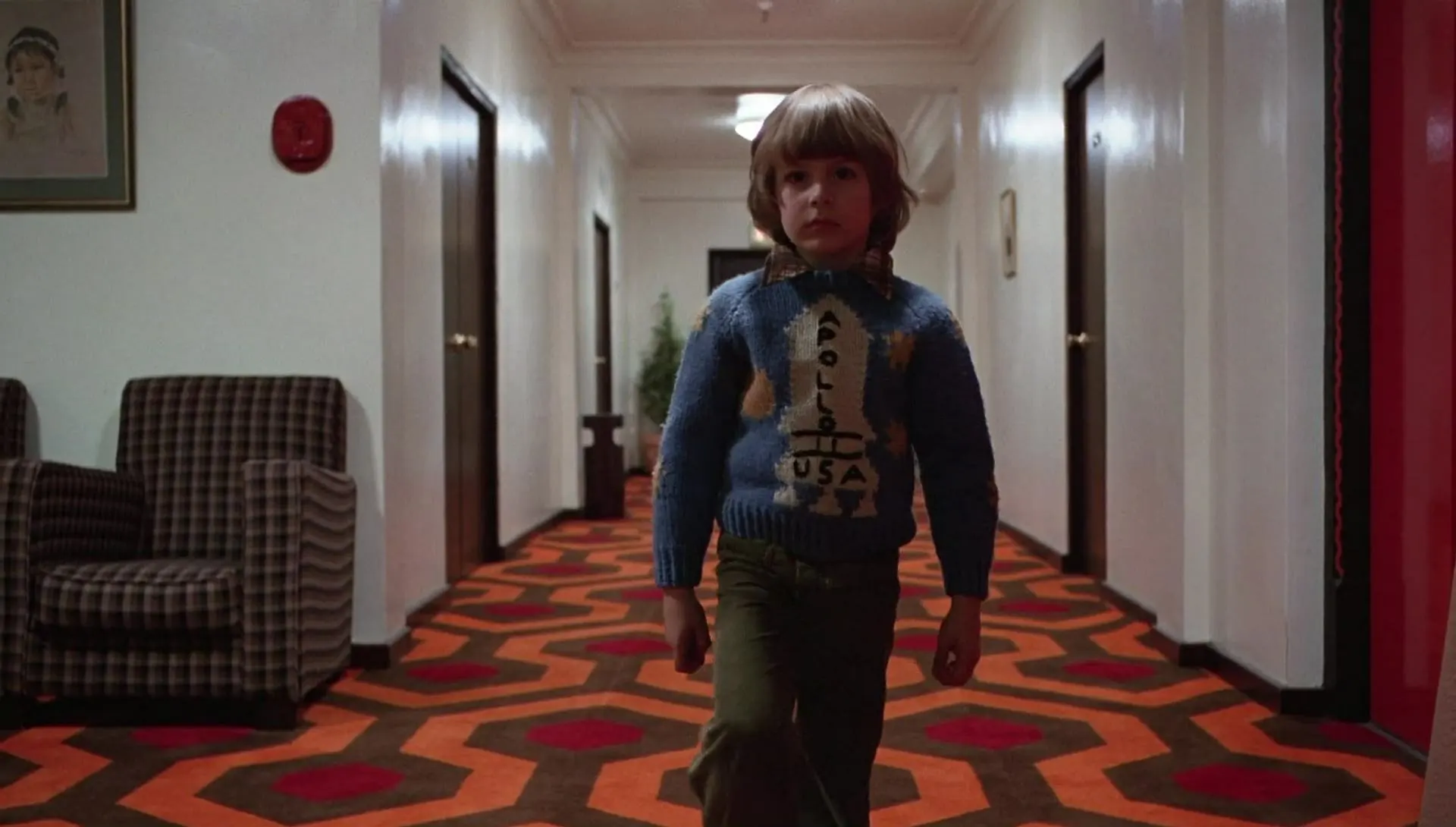
Another type of cinematographic shot is the wide shot, which has a descriptive function but, unlike the long wide shot, here the protagonist already acquires a certain weight in the scene. That is, it is recognizable but still has environment context.

PLANE FIGURE
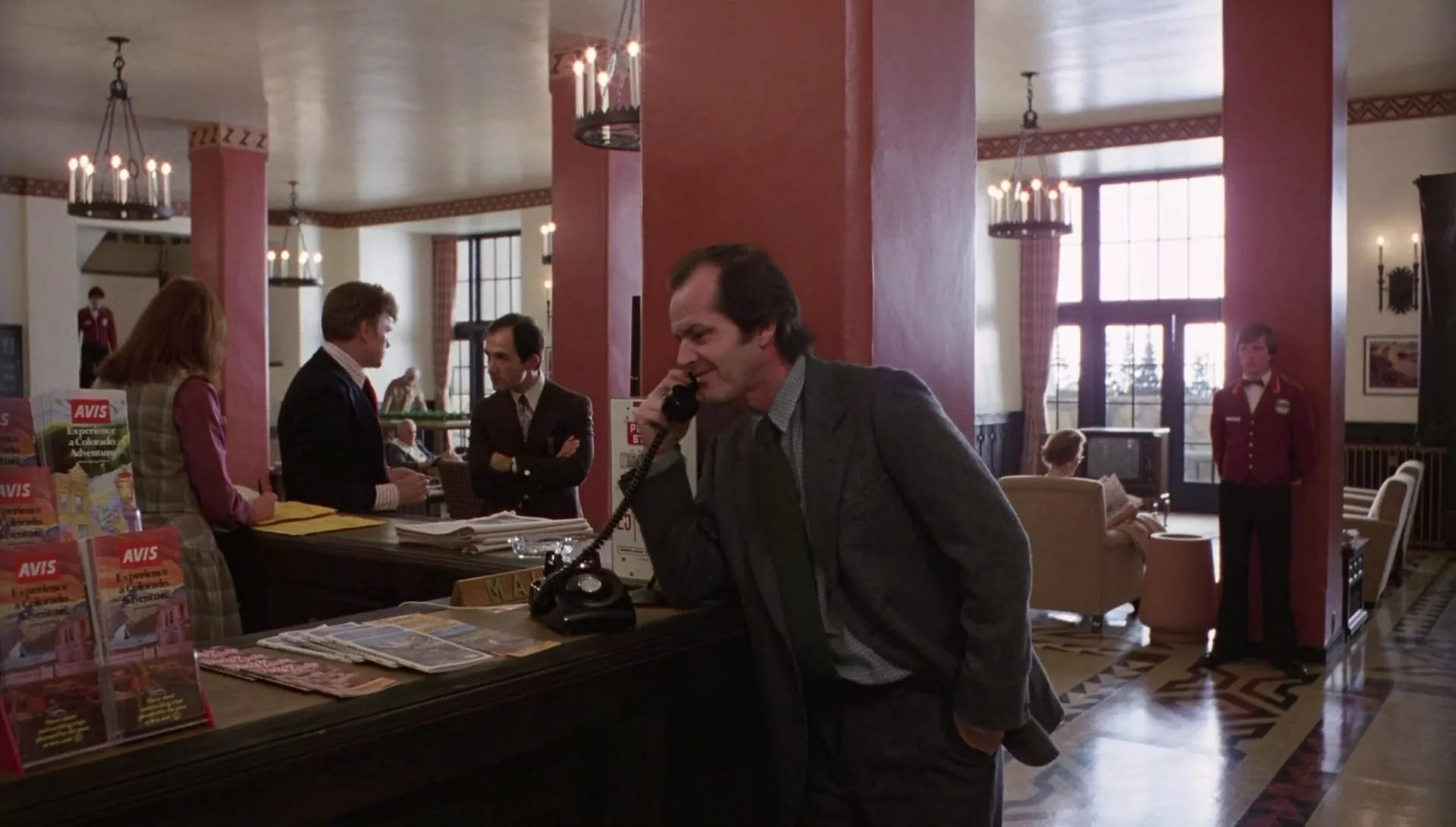
In this type of cinematographic shot, the figure takes on more prominence. This type of framing, also called a full shot, is limited at the top by the subject's head, and at the bottom, by his feet, thus gaining more importance on the figure and the clothing he might wear.

AMERICAN FLAT OR 3/4
Another of the types of planes that are most used in the cinema is the American plane or 3/4. In it, the frame is located approximately at the middle of the thighs.
This type of shot spread from cowboy movies because it allowed a good frame from the gun to the head and at the same time give some context to the scene.

MID SHOT
The medium shot is characterized by cutting the protagonist approximately in the waist area, leaving some air above the head.
This type of shot allows one or more protagonists to be appreciated in detail, to see their gestures, their features, while preserving information about the environment.
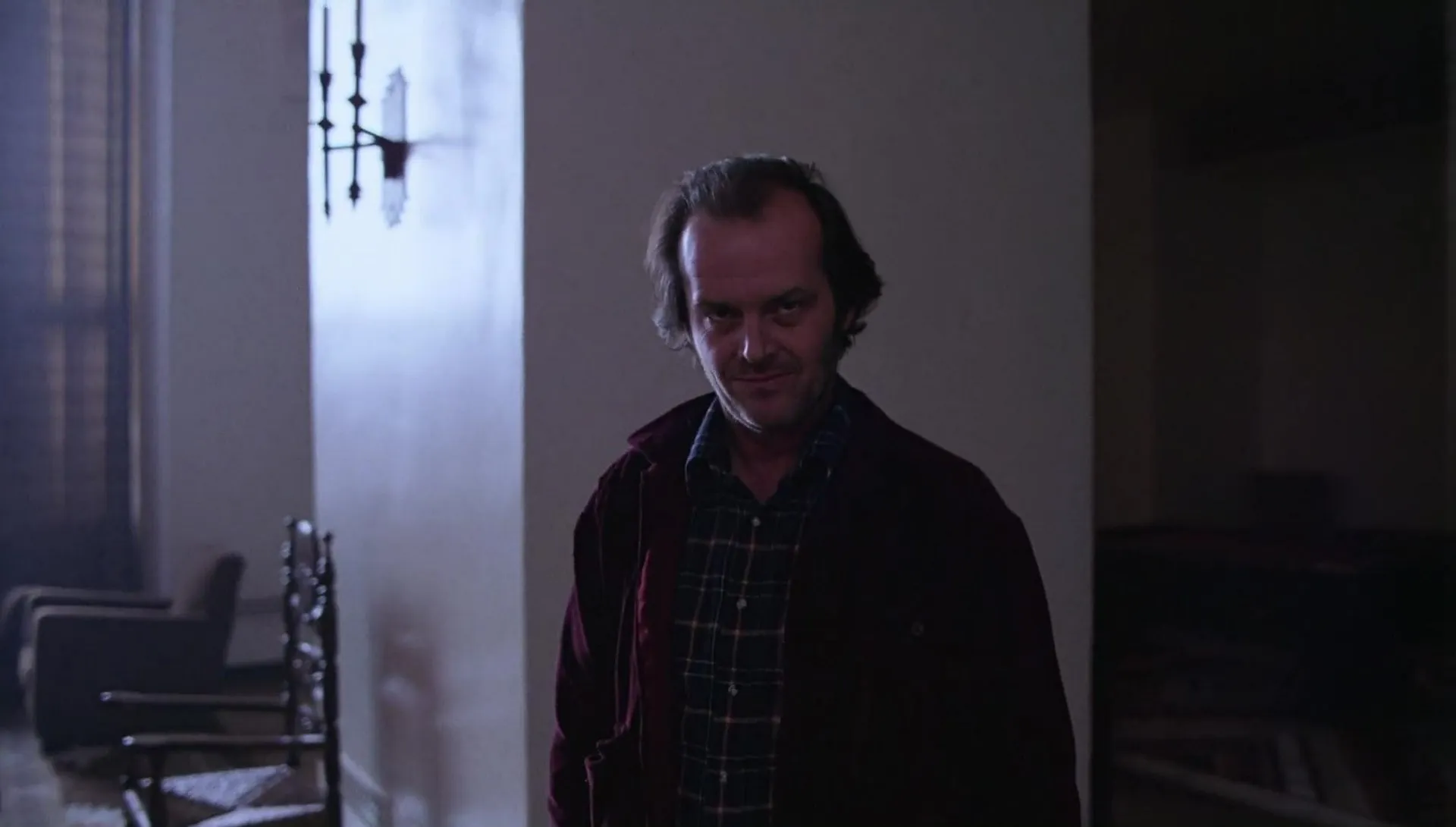

SHORT MEDIUM SHOT
Something more closed than the previous one, this type of cinematographic shot cuts the image through the chest of the protagonist (you will also find it for this reason, with the name of bust shot).
At the top, the image is limited somewhat above the head. This type of cinematographic shot focuses, now, all the attention on the protagonist above the environment.
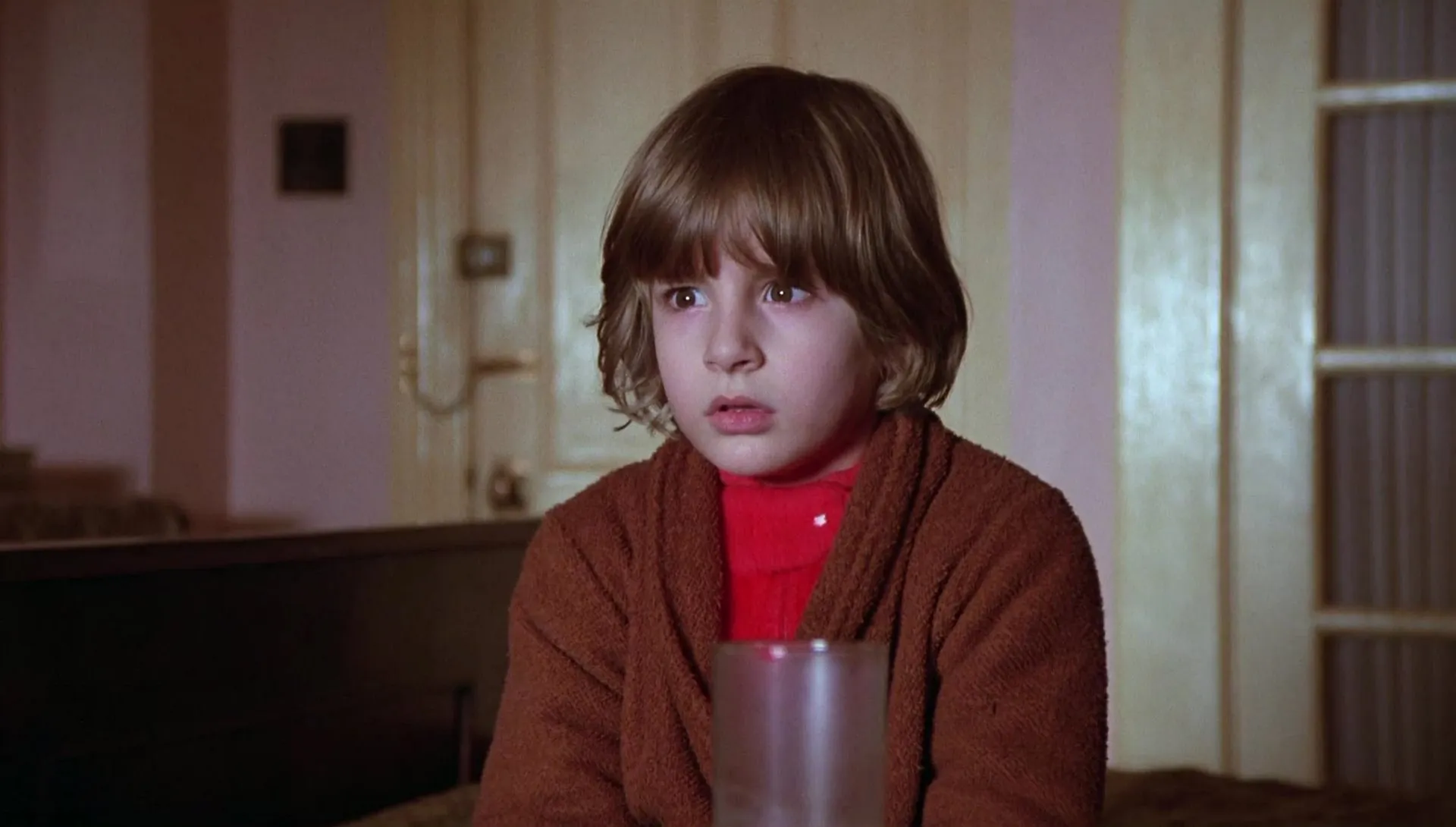

FOREGROUND
This type of shot focuses on the face of the protagonist. It is an intimate plane with which we can deduce feelings, focus on the look, the expression, etc.
This type of cinematic shot cuts the scene from approximately the shoulders of the protagonist to above the head.

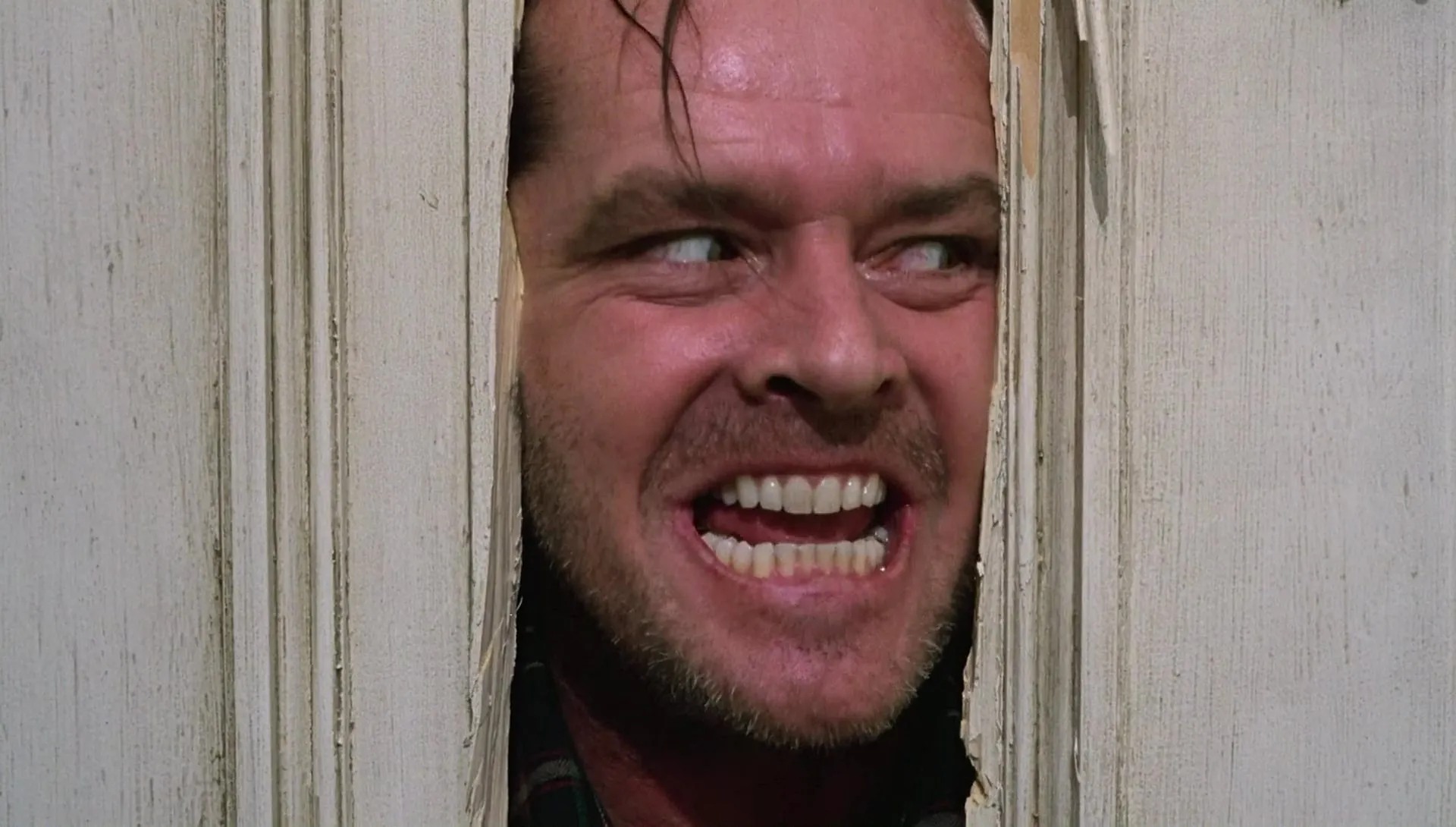
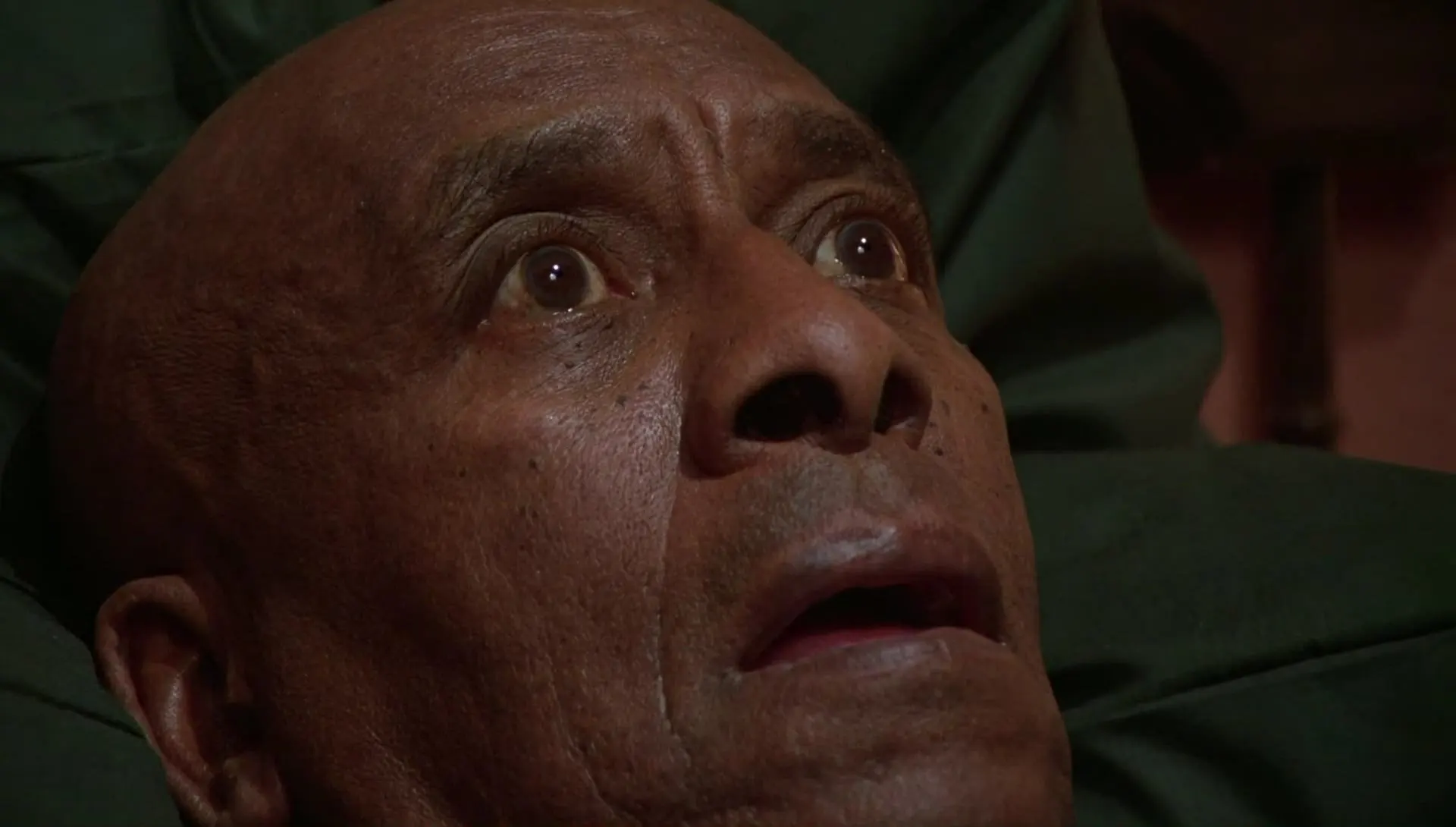
EXTREME CLOSE UP
At this point, the visual context of the scene has practically disappeared. We are immersed in the expression, in the reactions of the protagonists to what happens around them.
We are talking about a very intimate plane and with great drama , since the attention is focused exclusively on the feelings that the face of the actor or actress transmits to us.
This plane cuts the face roughly through the forehead and chin.


DETAIL PLAN
This is the plane used to emphasize the details of the narrative. They can be details of the subject or of the objects that you want to highlight.
It is usually used to give clues or focus attention on key elements for the development of the narrative.

FLAT SET
In this type of shot, two protagonists appear in the image, one closer to the camera and the other further away. This type of shot is used to show the interaction between two or more characters.
In the overall shot, the protagonist of the scene is closer to the camera, and the rest further away.

CINEMATOGRAPHIC SHOTS ACCORDING TO THE ANGLE
This type of planes used in the cinema (and also in photography), are classified according to the angle of the camera with respect to the subject.
The most common planes used in the cinema with respect to the angle are:
- overhead
- Chopped
- Normal
- low angle
- Nadir
Below, you can see how the camera is positioned in relation to the subject.
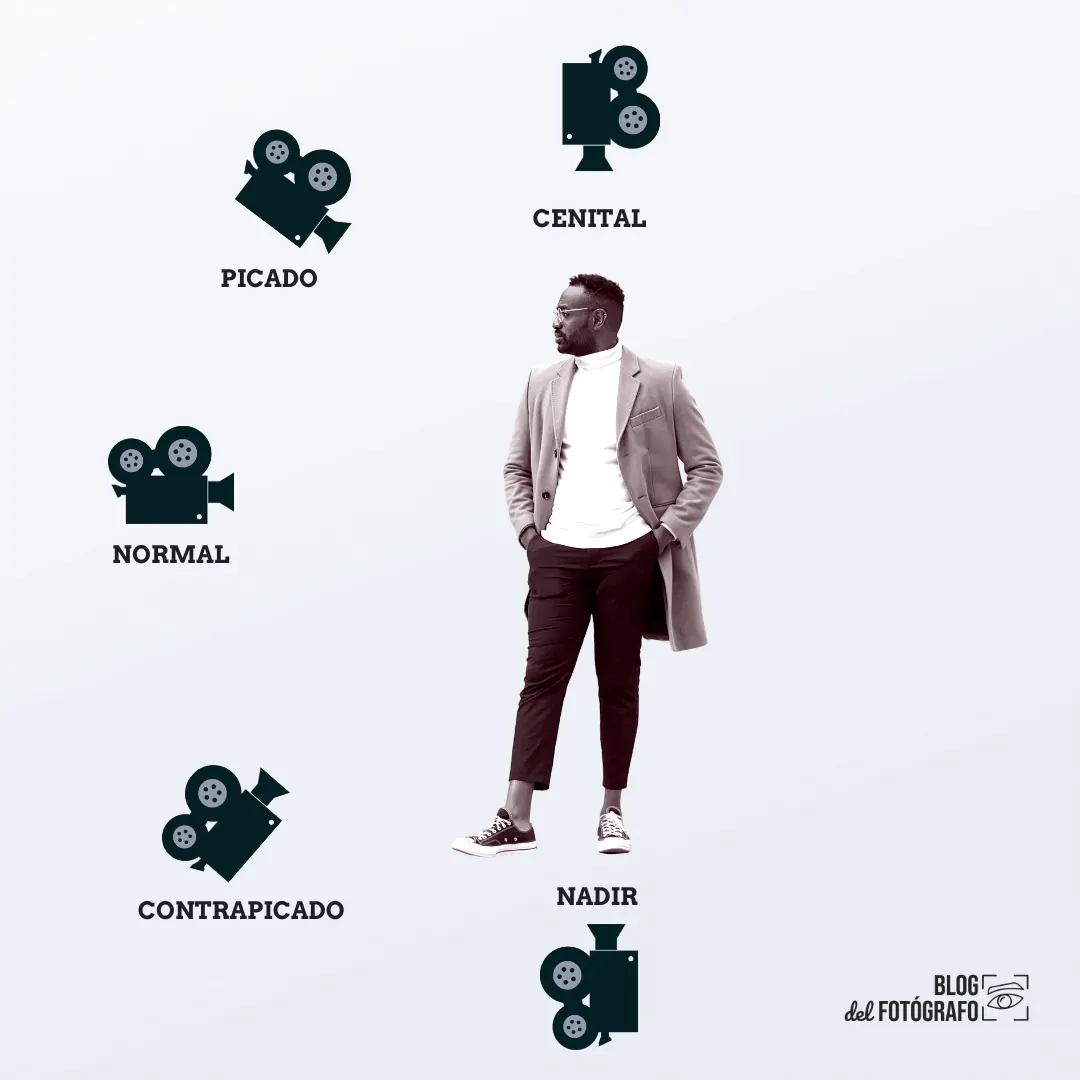
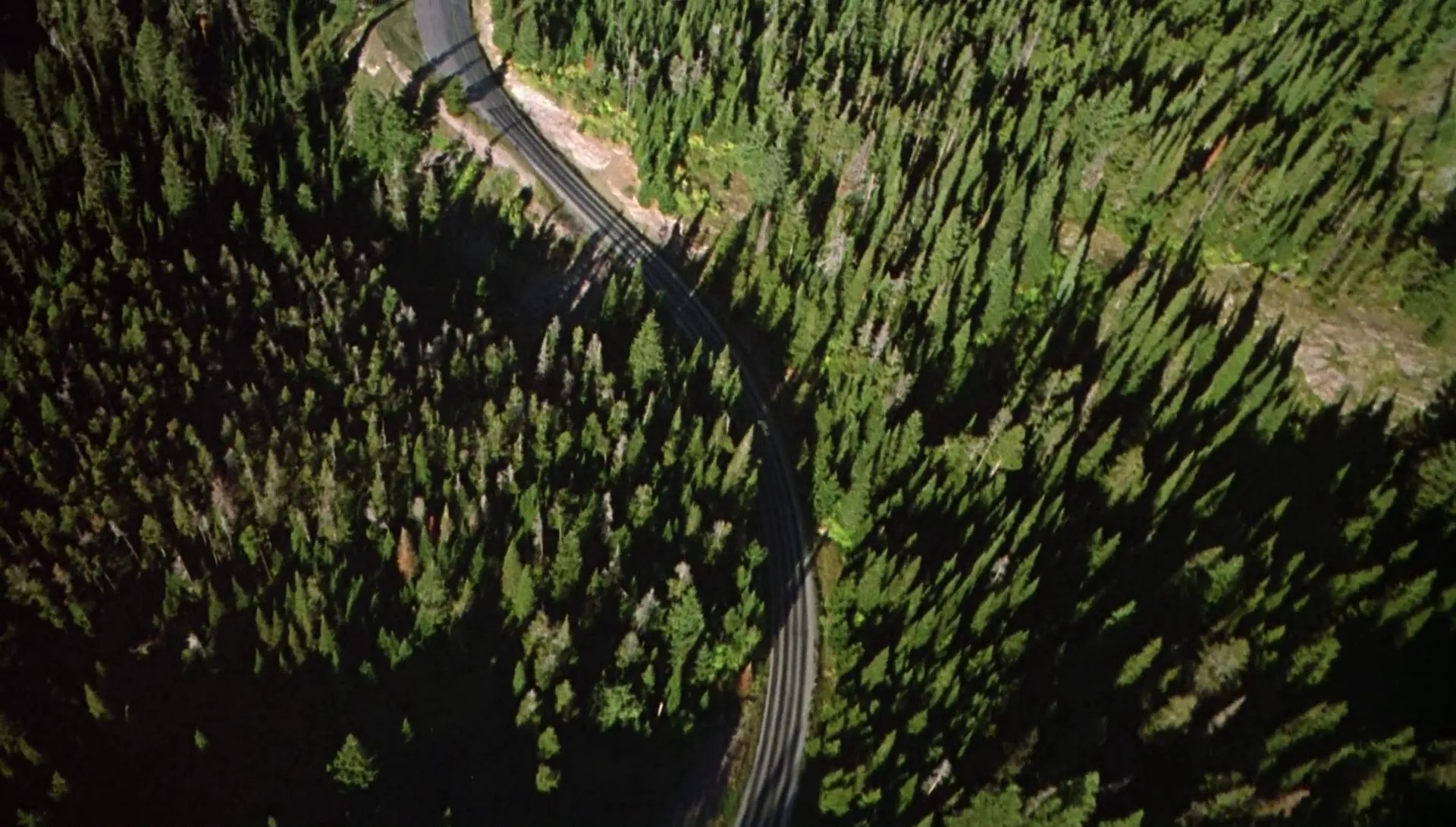
CENITAL PLANE
The zenithal plane is one in which the camera is placed completely above the subject or object, in a position of 90º with respect to it.
It is a descriptive shot that is usually recorded with drones or cranes, but also with standard cameras, as long as it is placed above the protagonist.
Depending on the altitude from which this plane is taken, you can find it as an aerial plane, very popularized by the rise of photography and video with drones.

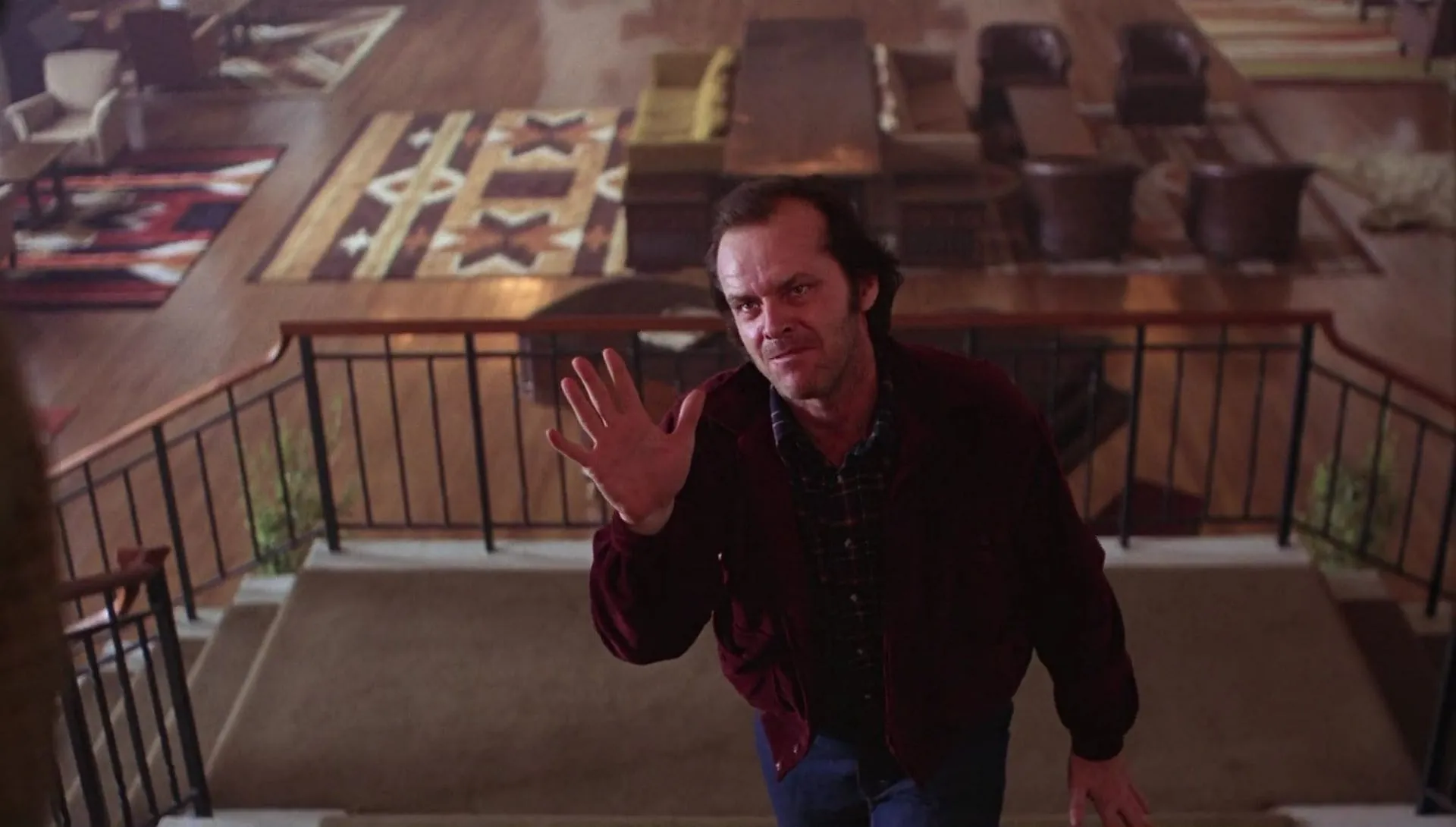
CHOPPED FLAT
A plane taken from above with an approximate inclination of 45º, which places us physically above the protagonist.
This type of shot transmits vulnerability, fear or fragility.

FRONTAL OR NORMAL PLANE
In this type of cinematographic shot, the camera is placed in front of the protagonist without any type of angle.
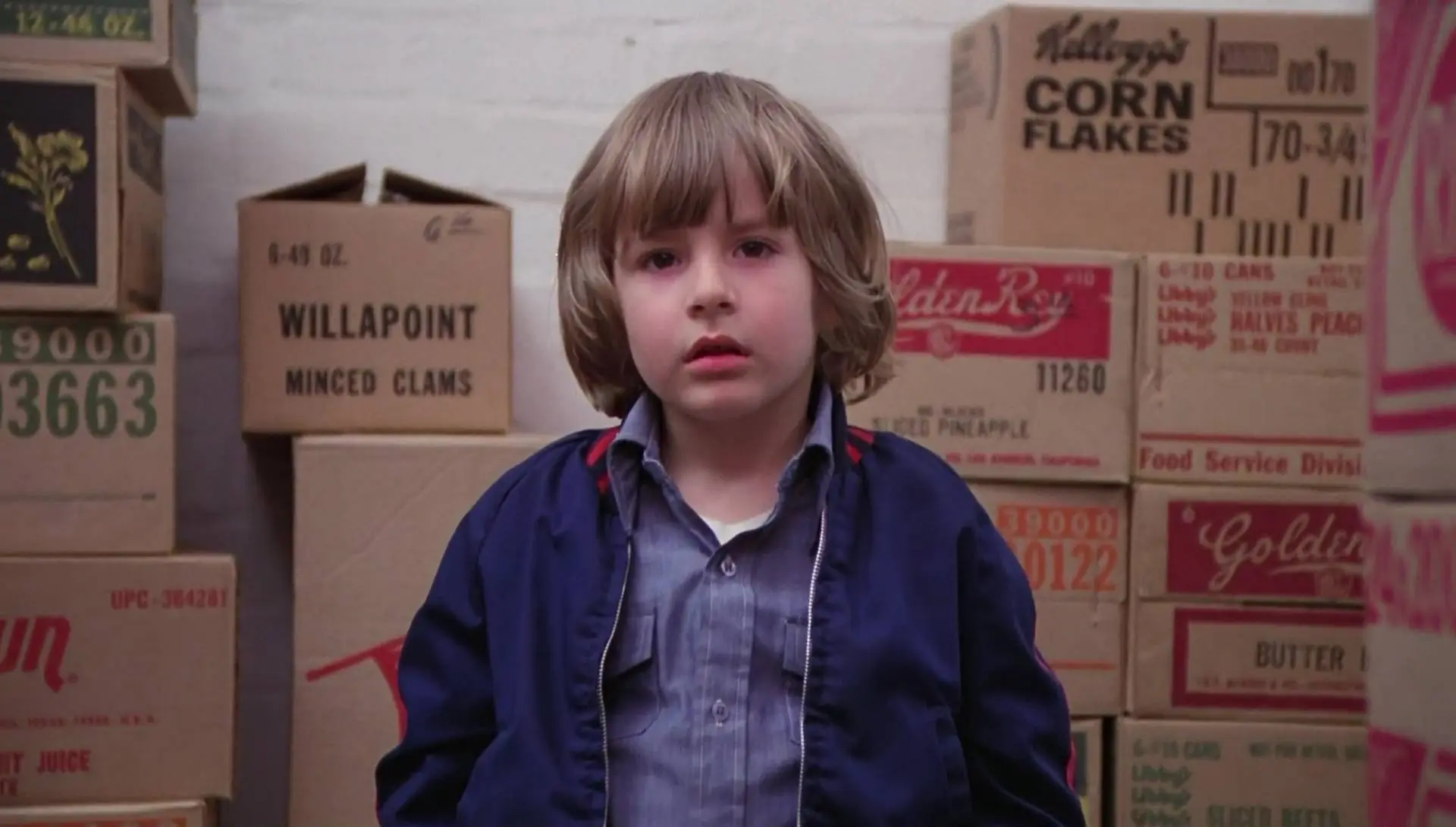

LOW ANGLE SHOT
Another type of cinematographic plane with the same inclination as the previous one (45º) but this time from below. It is usually used to show the power of the character, his superiority in some area or his heroism.
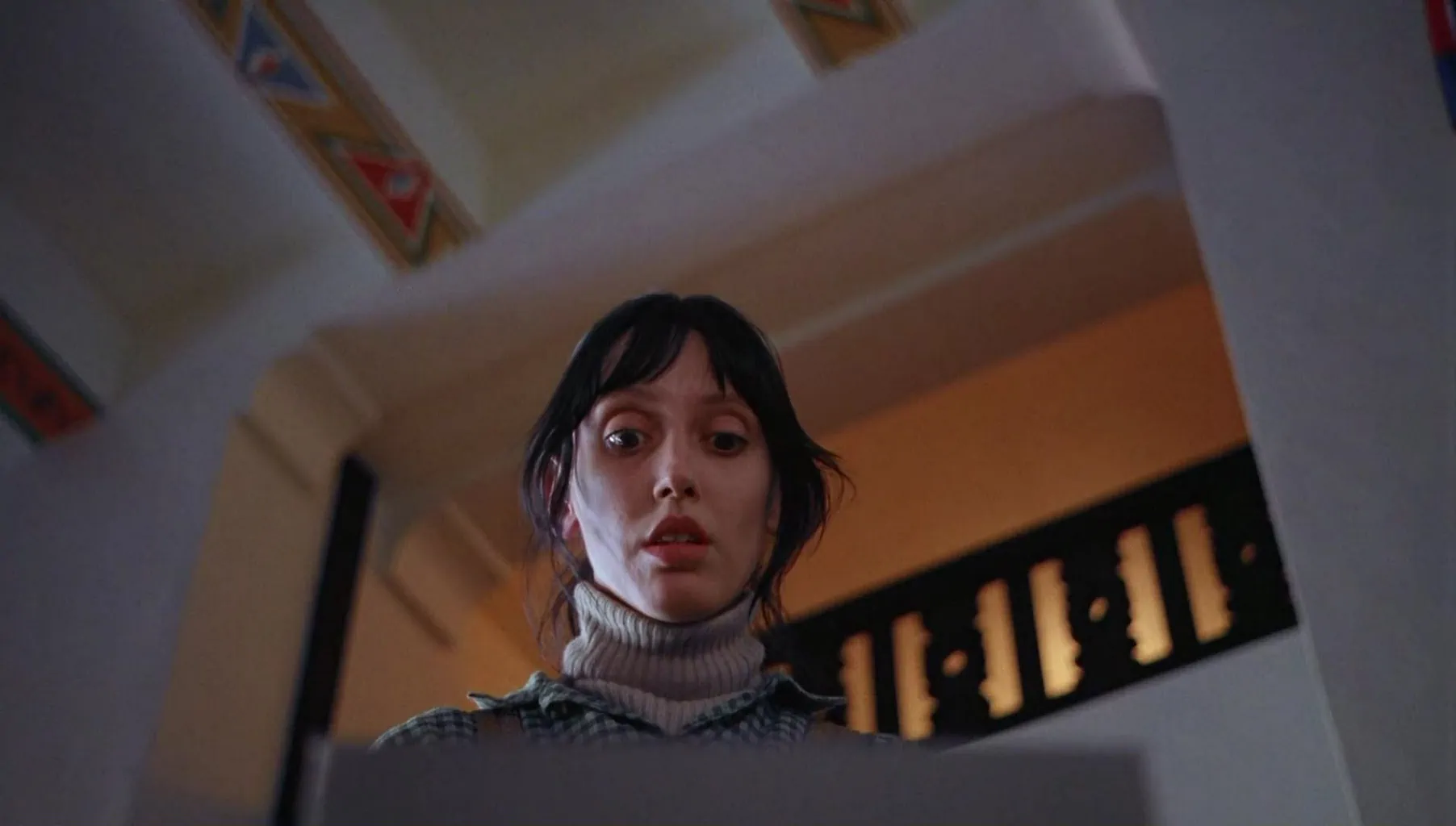

NADIR PLANE
This is a very extreme type of film shot used mostly for action scenes or high drama. It generates a deep sensation of vertigo.

After the most common ones, we have other equally interesting cinematographic shots for the narration, some due to the interaction of two people, follow-up shots, etc. Let's go see them.
FORESHORTENING PLANE
It serves to portray conversations or interaction between two people. The camera shows the person speaking from the front and in focus, and the person who is listening from behind and/or out of focus.
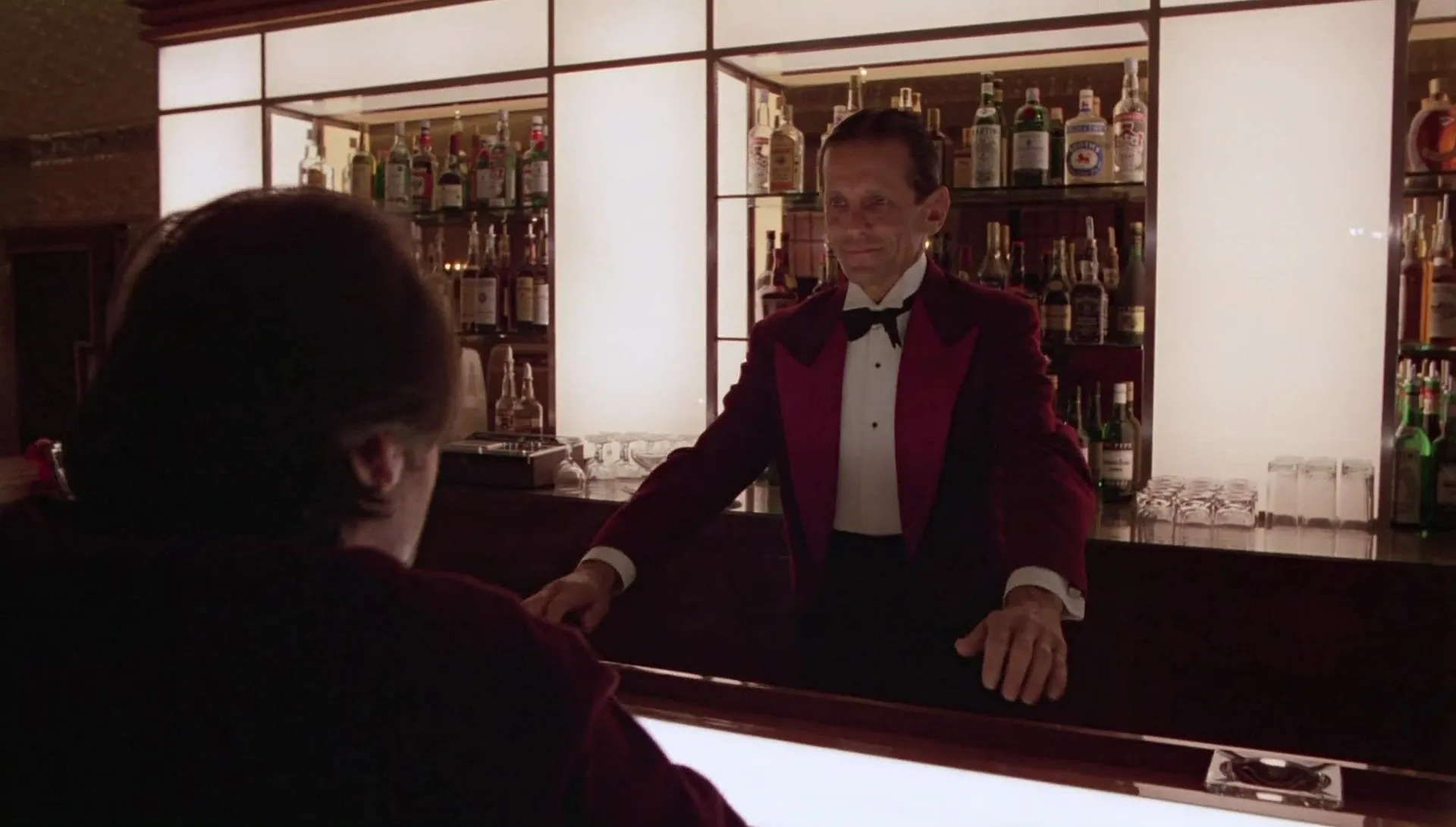

DORSAL PLANE
It is a plane in which the back of the protagonist is shown. It is usually a follow-up shot, used to give a sense of mystery and even fear.
This type of cinematographic shot introduces us into a scene full of tension where we know that something is about to happen.
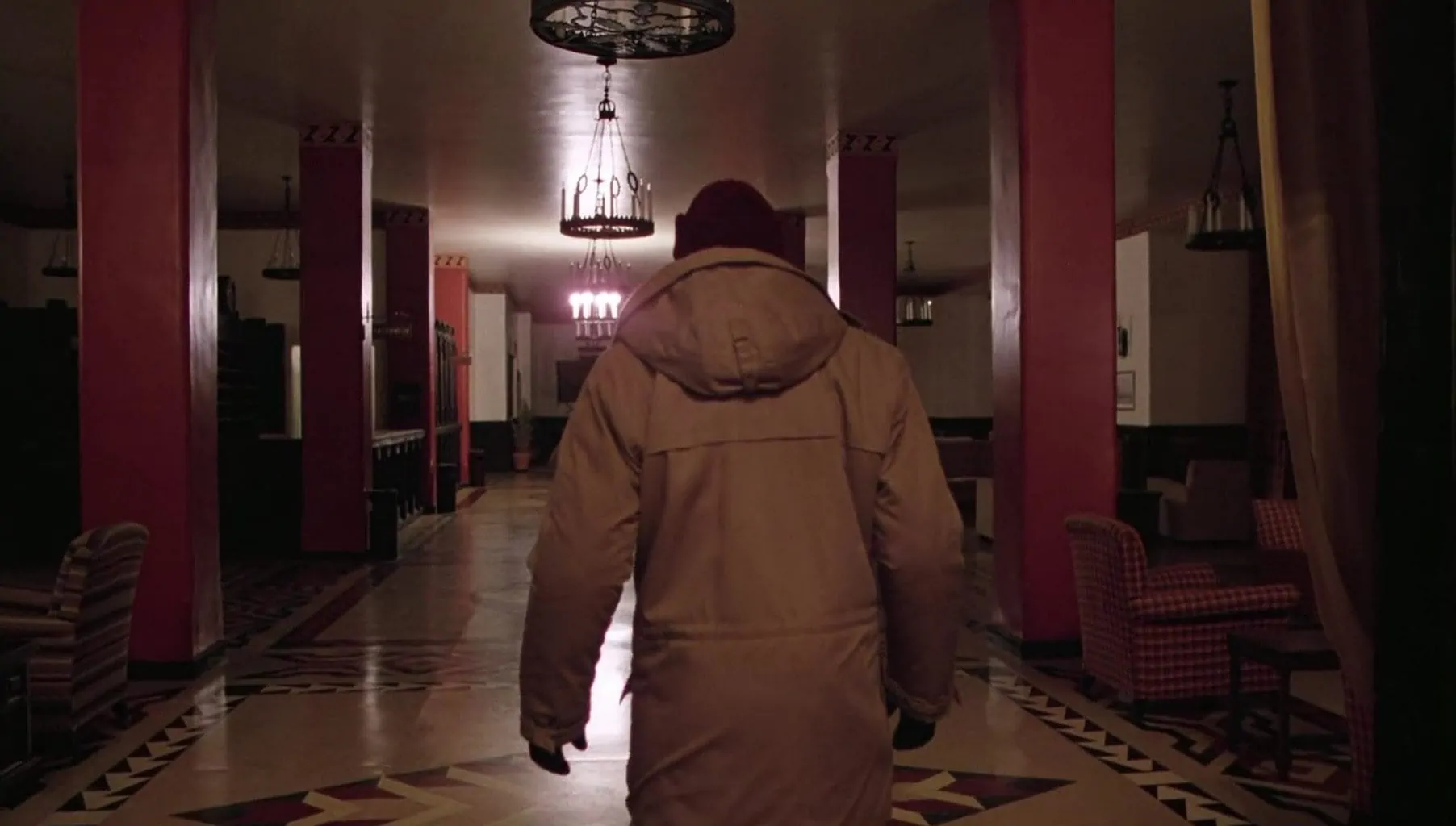

PROFILE PLANE
In this type of shot, the camera shows us the profile of the protagonist. Accompanied by the context or the lighting, it is a shot that can generate some mistrust towards the protagonist since we do not see it in its entirety.
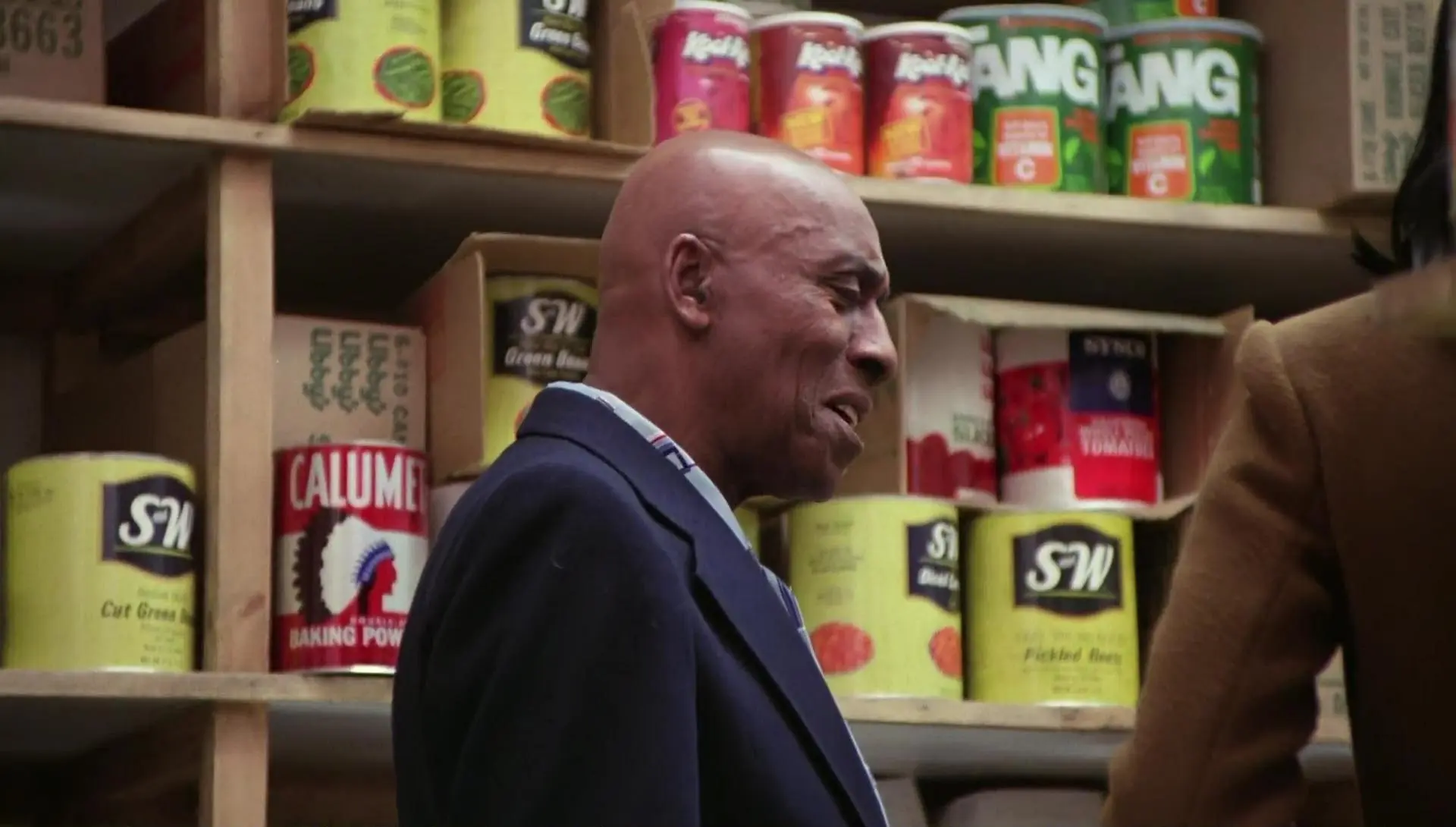

DUTCH PLANE
Another type of plane that is used in the cinema to transmit action where the camera tilts about 45º. It is a plane for action scenes and great drama.

TYPES OF PLANES ACCORDING TO THE POINT OF VIEW
Depending on how we want the viewer to participate in our recordings, we will choose one point of view or another. Let's see how to do it through the plans.
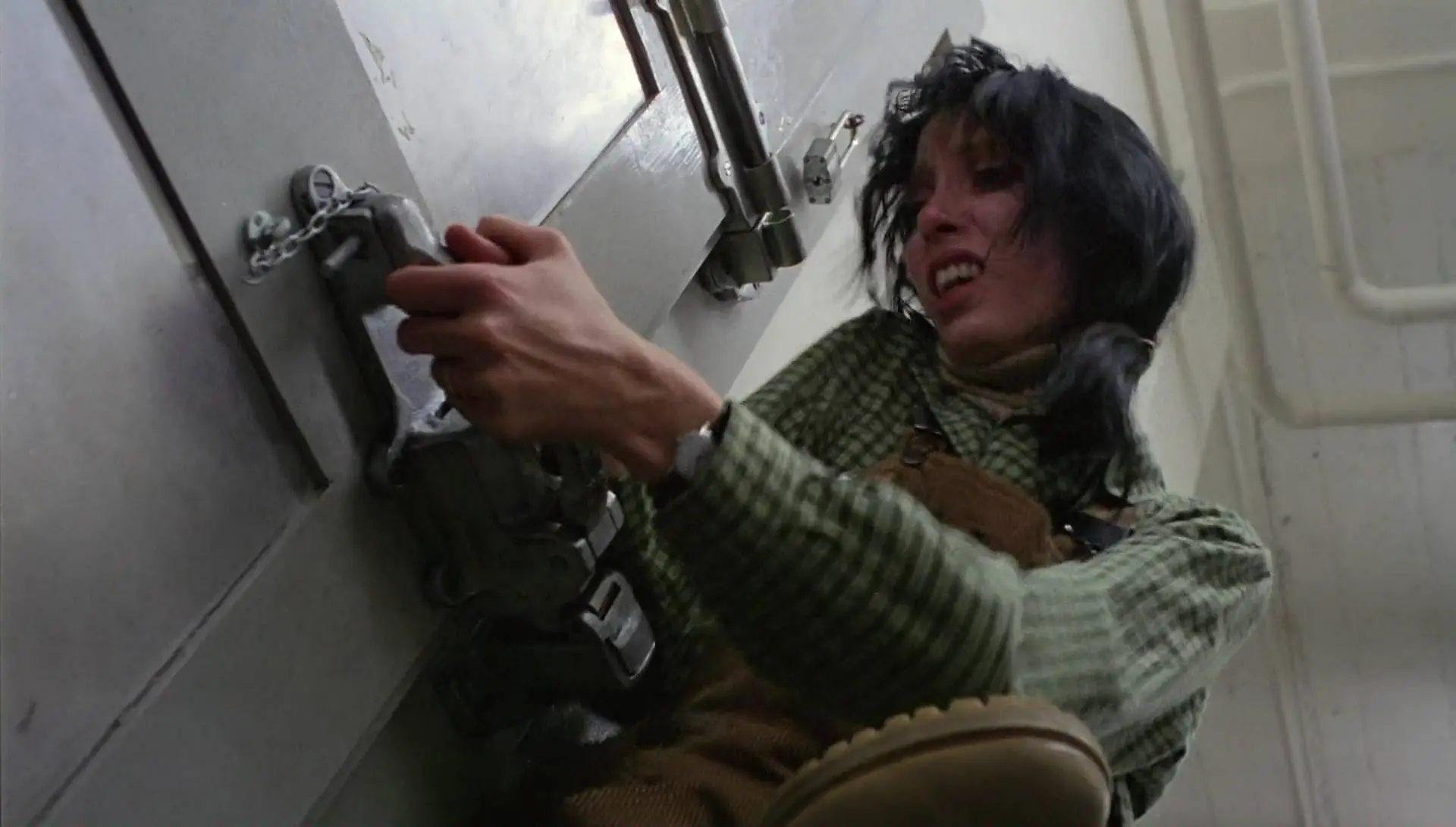
TARGET PLANE
This type of plan is the most common. It represents the point of view of someone looking at the image but not appearing in the scene.
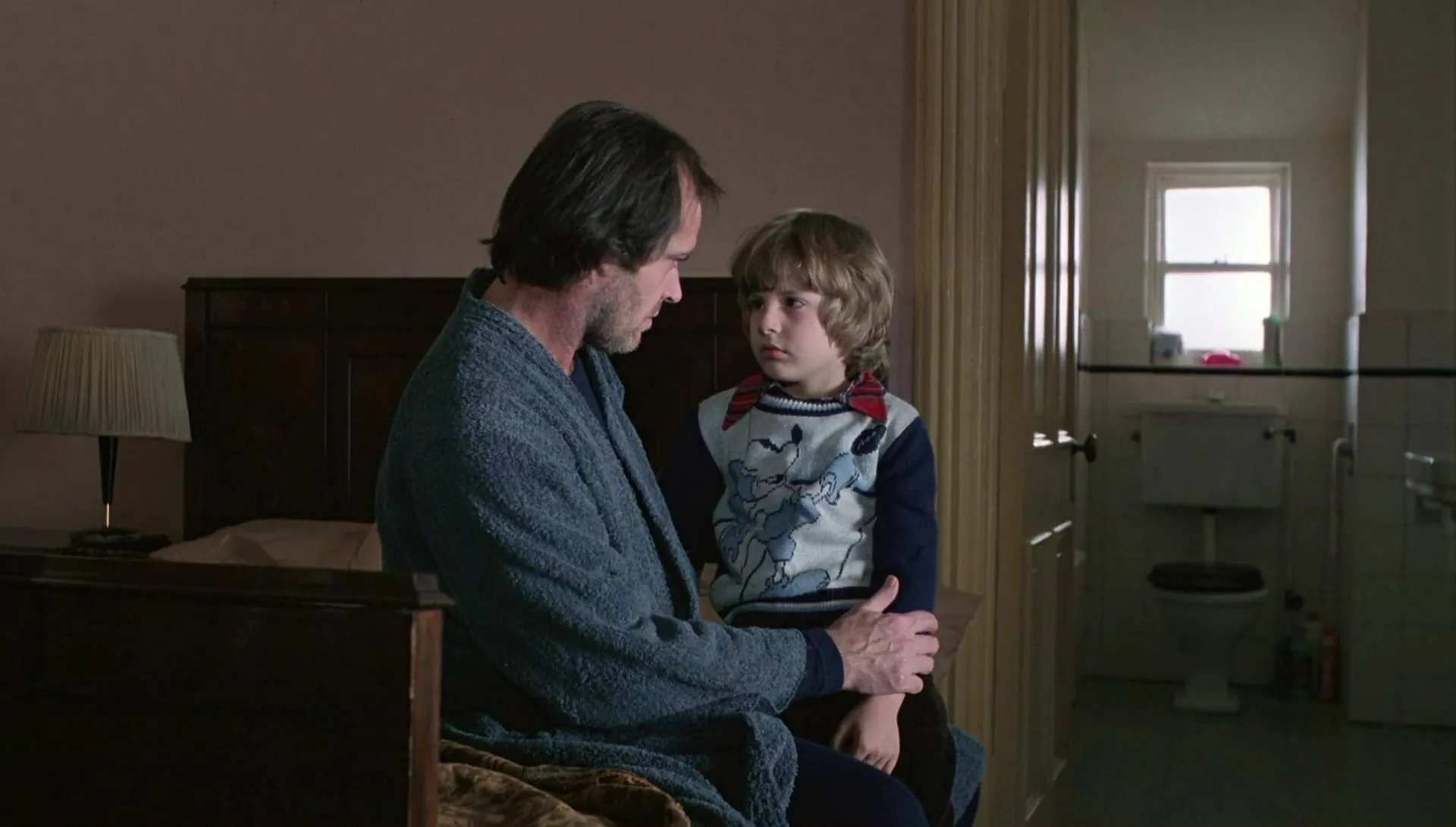

SUBJECTIVE SHOT
The scene is shown from the point of view of one of the characters. The viewer sees through the eyes of the protagonist.

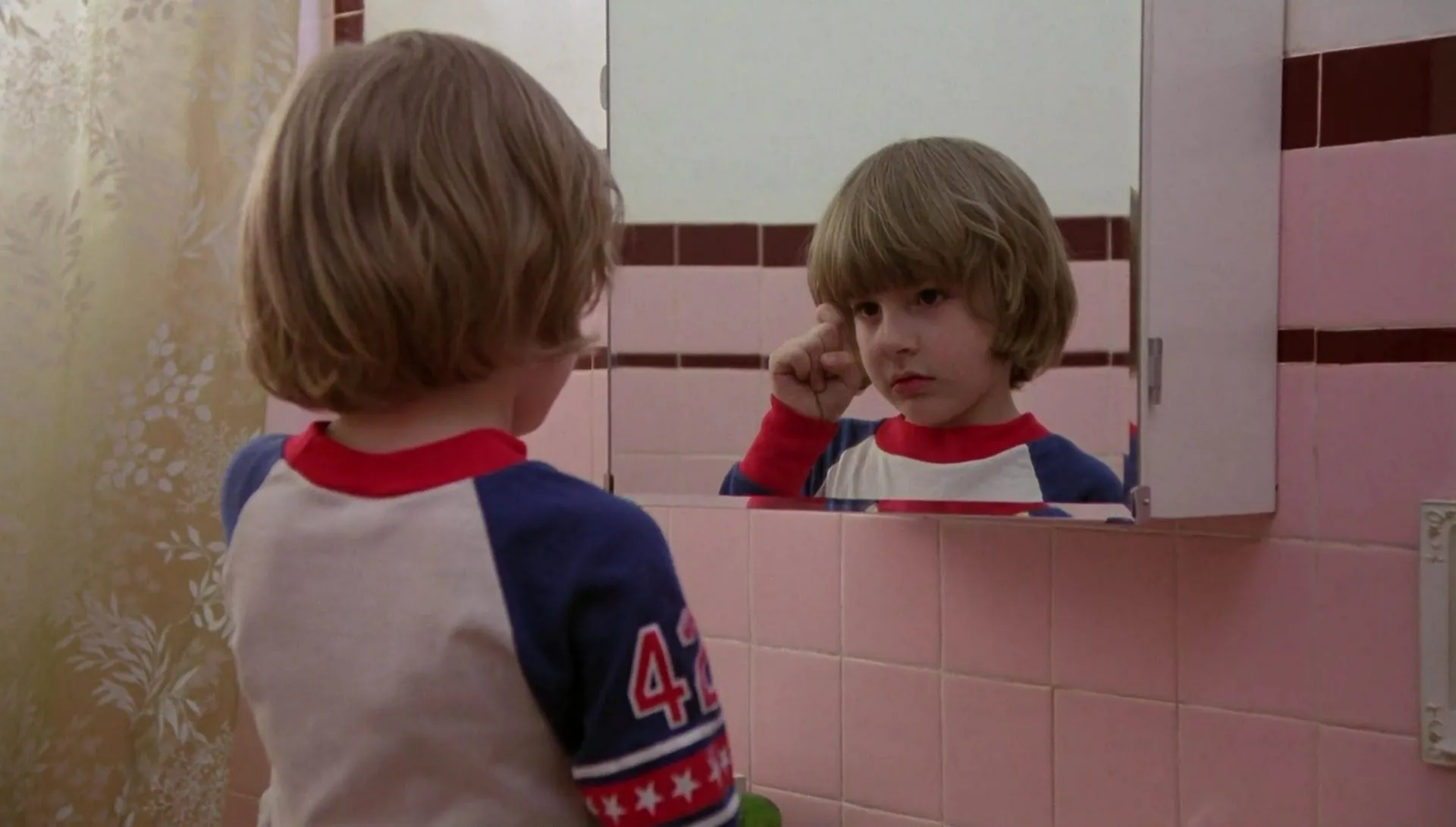
INDIRECT PLANE
Reflections are a great cinematic resource. The indirect plane is the one that is generated through a reflection.

The types of shots in photography have a lot in common. If you are interested in plans specifically in photography , do not miss the link article.
What do you think? Did you know all the types of film shots in this article? The next time you see a movie, would you dare to search and analyze the types of shots that appear?
The best way to assimilate any type of content is by practicing, so I encourage you to do so. I hope this article has been useful to you. If so, share it on your favorite social networks or with whoever you think might be interested.

![TYPES OF SHOTS IN FILM [WITH EXAMPLES INCLUDED]](https://photographychef.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/TYPES-OF-SHOTS-IN-FILM-WITH-EXAMPLES-INCLUDED.jpg)
